Lyxor MSCI Indonesia UCITS ETF (INDO) - 07/12/2018
Short Term strategy: Positive (90%) / Trend =
Long Term strategy: Positive (60%) / Trend +
Characteristics of the ETF
The INDO ETF (Lyxor UCITS) created in 07/2011 and which is listed in Euro on Euronext replicates the index MSCI Indonesia Net Total Return, denominated in USD which is the benchmark index of the Indonesian stock exchange made up of the 29 principal stocks in terms of market capitalization adjusted for free float and liquidity.
The ETF's fees are 0.45% and the AUM are 44M €. The replication method is indirect (via a swap) and there is a dividend capitalization policy.
Alternative ETFs: EIDO (iShares in USD)
Index & components
INDO replicates an index of which 43.8% of the capitalization depends on the Financial sector, essentially the 4 main banks of the country of which the biggest, Bank Central Asia represents 16% of the index.
Alongside the banks, three sectors account for most of the capitalization: durable consumer goods (14.7%), telecoms (13%) and consumer discretionary goods (1.7%). This tracker naturally embeds the risk related to the Indonesian rupiah, more volatile than the reference currencies. Indonesia has experienced a GDP growth rate of 5.1% in 2017 reaching $ 980 billion, driven by household consumption, the domestic market is strong of its 257 million inhabitants of which nearly 70 million belonging to the middle class. The government has embarked on a policy of economic openness and deregulation since September 2015 and encourages the participation of foreign investors.
Negotiations with the European Union to conclude a free trade agreement began in the autumn of 2016. Indonesian exports are large (176.3 billion USD) but with a strong dependence on raw material exports . Indonesia has considerable agricultural resources (palm oil, natural rubber, cocoa, coffee), energy and mining (coal, oil, liquefied natural gas). It is the world's second largest exporter of coal and the sixth largest producer in the world. Imports amount to 178.2 billion USD, mainly composed of intermediate goods. President Jokowi has developed a social security system for poor households and also encourages the participation of foreign investors in financing infrastructure (such as the construction of a real railway network in Sumatra).
Indonesia's foreign policy, an emerging power and member of the G20, aims to play an active role on the international and regional stage. Beijing is Jakarta's largest trading partner and also its largest supplier (21% market share). Indonesia, the second recipient of Australian aid (AU $ 365 million in 2016-17), is also Australia's top priority in the region and the two countries are linked by a strategic partnership. The exchanges with Japan, the first donor of bilateral aid to Indonesia (28.9% of the aid received by Indonesia), have been part of a strategic partnership since 2006, particularly in the field of connectivity in the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.
The Indonesian currency remains dependent on short-term capital flows and could depreciate in the event of a rise in overall risk aversion, which would improve the competitiveness of Indonesian exports but could generate additional inflation. Nevertheless, the situation has improved since 2015, the authorities have implemented a more prudent monetary policy, the current balance has recovered and foreign exchange reserves have increased (8 months of imports in 2017). But further reforms are still needed to limit exchange rate vulnerability through investment liberalization, including relaxing the rules for foreign investors and lifting the ban on exports of raw minerals.
Latest developments
INDO's performance in 2017 was + 8.2%, after an increase of + 20.8% in 2016, but fell by -7.8% in 2018, due to fears of a trade war, the sharp rise in US dollar and US long interest rates.
However, unlike the major world markets that have corrected sharply since October, the Indonesian index has rebounded at the same time, which is linked to the decline in oil prices. Indeed, oil is, as for India the first import item, with negative effects on the balance of payments and the currency, in case of soaring crude prices. Conversely, the fall in oil prices is a very favorable factor for the country, which supports its currency at the same time.
The main uncertainties concern the evolution of the monetary policy of the US Federal Reserve and possible new episodes of downward pressure on the rupee. Chinese growth is also a key factor for the evolution of the Indonesian economy.
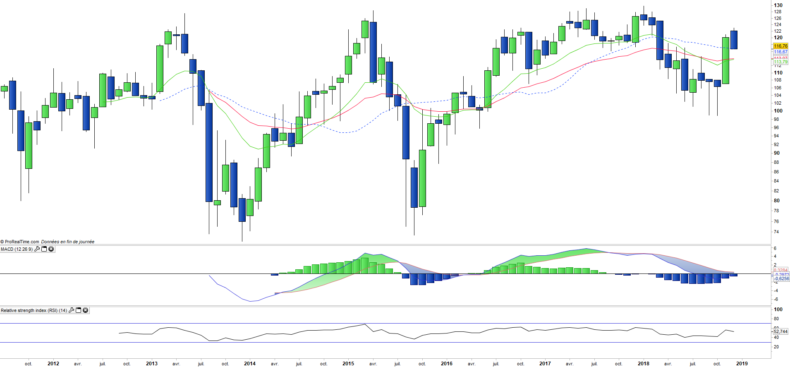
Monthly data
The monthly chart shows a long-term trend fairly flat, but well oriented for two months. Consolidation is in progress after the October’s breakthrough, which should lead to the crossing of EMAs13 and 26, which would be a confirmation of the change in trend. However the long-term resistance located at € 130, and valid for more than 5 years will be difficult to overcome.
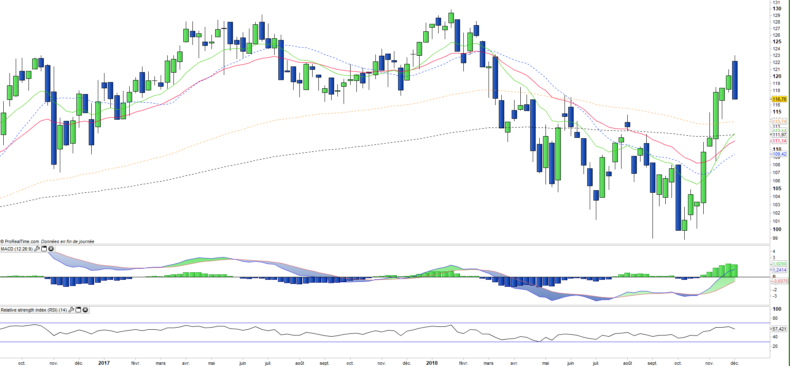
Weekly data
On the weekly chart, we can see the medium-term bullish reversal that propelled the index above all its moving averages and reverse all the technical oscillators positively. However a bearish engulfing pattern is in formation, and if confirmed at Friday closing would be a signal of short-term consolidation towards EMAs13 and 26.
ETF Objective
INDO is a UCITS ETF which seeks to replicate MSCI MSCI Indonesia Net Total Return
Characteristics
| Inception date | 04/07/2011 |
| Expense ratio | 0,55% |
| Issuer | Lyxor |
| Benchmark | MSCI Indonesia Net Total Return |
| Code / Ticker | INDO |
| ISIN | FR0011067511 |
| UCITS | Yes |
| Currency | € |
| Exchange | Euronext Paris |
| Assets Under Management | 43 M€ |
| Replication Method | indirect (swap) |
| Dividend | Capitalization |
| Currency risk | Yes |
| Number of Holdings | 28 |
| Risk | 4/5 |
Country Breakdown
| Indonesia | 100% |
Sector Breakdown
| Financials | 44% |
| Consumer staples | 15% |
| Telecommunication services | 13% |
| Consumer discretionary | 11% |
| Materials | 7% |
| Energy | 5% |
| Others | 5% |
Top Ten Holdings
| Bank Central Asia | 16% |
| Bank Rakyat Indonesia | 13% |
| Telekomunikasi Indonesia | 12% |
| Astra International | 10% |
| Bank Mandiri Persero | 9% |
| Unilever Indonesia | 4% |
| Bank Negara Indonesia | 4% |
| Charoen Pokphand | 3% |
| United Traktors | 3% |
| Gudang Garam | 3% |