ETN iPath Bloomberg COCOA Subindex - NIB - 14/03/2018
Short Term strategy : Positive (100%) / Trend +
Long Term strategy : Positive (70%) / Trend +
Characteristics of the ETF
The NIB tracker is an ETN (exchange traded note) which is listed on the NYSE in USD, a product similar to an ETF, with the difference that an ETN is more like a bond in the sense or if the issuer goes bankrupt (in the Barclays occurrence) the capital loss is total. The quality of the issuer is therefore important, and in the case of one of the main UK banks, the risk associated with the issuer is extremely low. However, the product may be sensitive to a downgrade of its credit rating.
This ETN reproduces a set of future contracts on cocoa prices which constitutes a relatively faithful exposure to the prices of this agricultural raw material.
The fees of this ETN amount to 0.7% while the current AUM is $ 56M. The most important trading places for cocoa trading are the New York Board of Trade (Coffee Branch, Sugar and Cocoa Exchange, abbreviated CSCE) and LIFFE London. Cocoa is traded in dollars per ton, but future cocoa contracts are for 10 tons.
Alternative ETFs: COCO (ETFS in USD), SHOCK (iPath in USD)
Latest developments
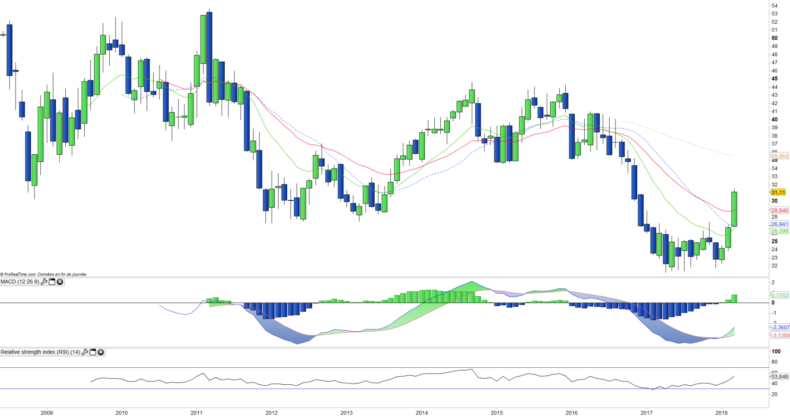
After 4 years of increase between 2012 and 2015, Cocoa prices collapsed in 2016, which resulted in a -34.9% fall on NIB then -15.1% in 2017, but the rebound started in 2018 and NIB is up 36% since the beginning of the year.
Demand remains strong and should continue to grow at the pace of global growth, but the big unknown is the supply and especially that from African producing countries, where the majority of world production is concentrated (about 70%).
The Cocoa bean is supported by the decision of Ivory Coast, the world's largest producer, to bring down the country's cocoa production over the next five years. At the International Agricultural Show (SIA), the Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development, Mamadou Sangafowa Coulibaly, has indeed announced this policy to improve the quality of cocoa ... and probably to support the price.
Index & components
Cocoa refers to cacao beans, which grow mainly in tropical forests, and the powder obtained after roasting and grinding these beans. Africa's top cocoa producers are Ivory Coast (40% of world production) followed by Ghana (around 20%), cocoa is also produced in Asia (Indonesia and Malaysia) and in South America (mainly Brazil). Cocoa is imported mainly in rich industrialized countries such as the United States and Europe where it is Germany that imports the most.
Most of the world's cocoa production is turned into chocolate, with only a third of it being cocoa powder for chocolate drinks. From cocoa beans, it is possible to produce cocoa powder or cocoa butter. In recent years, the industry has discovered several substitutes for cocoa butter in chocolate production, so demand for real cocoa butter has declined sharply. It is for this reason that cocoa farmers are now focusing their attention on cocoa powder.
In the late 1980s, the state-controlled market was liberalized under pressure from the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund, allowing major international producers to enter the market. The world market is worth $ 3 billion a year with a very volatile cocoa price that could have risen to $ 3,000 per ton in the 1970s, but has since been in the range of $ 1,000 to $ 2,000 per ton. After a peak in 1977, cocoa prices declined to collapse in the 1990s. This was due to world production above consumption on a recurring basis and the accumulation of surpluses from previous years. The chronic imbalance between supply and demand on the cocoa market causes large price variations. The life cycle of a cocoa tree (which yields an interesting harvest only after six years) does not allow those who cultivate it to react rapidly to changes in demand. Climate and pests are also factors that make price changes unpredictable. Thus, parasites and diseases cost an average of about 30% of world production, for example the swollen cocoa shoot virus (CSSV) seemed to have disappeared in the 1950s but resurfaced in 2003 in Ivory Coast.
In terms of forecasts, growth in demand is expected to increase slightly by 2 to 3% per year worldwide and will be particularly strong in the Asia region, whose demand for cocoa could grow by 4% per year. The increase in cocoa consumption is also very important in emerging countries: in 5 years, this increase has been 75% in China, 80% in India and 23% in Brazil which are experiencing an increase in incomes, a development of middle classes and a standardization of tastes. If this evolution were to continue, it could in the medium-term cause tensions on the price of this raw material which could become a rare commodity.
Monthly data
The monthly chart shows a dramatic reversal of the bearish trend since the beginning of 2018. In 2 months, prices have crossed all moving averages, the technical oscillators have turned around and a rounded bottom pattern has formed to a bullish breakout towards the $ 35 pivot zone. The prices must confirm the reversal in process, but the change of trend is already almost recorded.
Weekly data
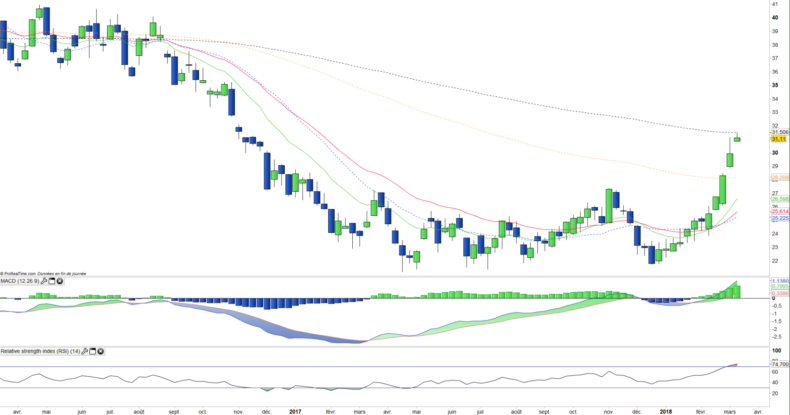
On the weekly chart, we can see the very strong upward momentum since the beginning of February which allowed the courses to exceed all moving averages. Prices are now reaching the level of the EMA200 which could cause a short-term correction to the EMA100 at around $ 28 which would be an interesting level of intervention in the perspective of a continuation of the bullish movement.
ETF Objective
NIB is an ETN listed in $, which seeks to replicate the Bloomberg Cocoa Subindex Total Return
Characteristics
| Inception date | 24/06/2008 |
| Expense ratio | 0,70% |
| Issuer | Barclays |
| Benchmark | Bloomberg Cocoa Subindex Total Return |
| code/ticker | NIB |
| ISIN | US06739H3131 |
| UCITS | No |
| Currency | USD |
| Exchange | NYSE Arca |
| Assets Under management | 56 M$ |
| Dividend | No |
| Currency risk | No |
| Number of Holdings | NS |
| Risk | 4/5 |
Country Breakdown
| USA | 100% |
Sector Breakdown
| Cocoa | 100% |
Top Ten Holdings
| Cocoa | 100% |